Da-TRASH: Depth-appended Tabletop Recycling Algorithm for Segmenting Havoc
Abstract
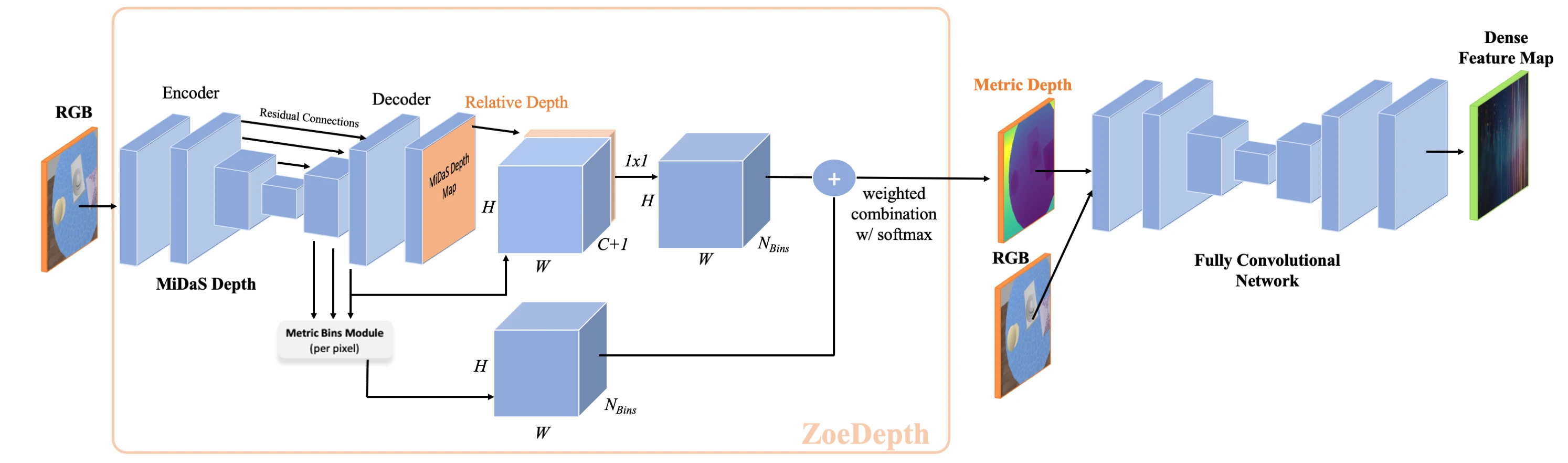
In this work, we set out to reproduce and build upon the results presented in Learning RGB-D Feature Embeddings for Unseen Object Instance Segmentation (Xiang et al., 2021). This previous work makes use of deep learning and non-photorealistic, synthetic RGB + Depth data to produce surprisingly accurate instance segmentation masks for previously unseen objects. In this report, our team validates the previously published results that suggested combining RGB and depth feature vectors elementwise is most effective for the task of unseen object instance segmentation (UOIS). Additionally, our team extends upon previous work by adapting the existing UOIS model such that it can perform segmentation on RGB-only images. By fusing the RGB-only input images with output from a monocular depth estimation sub-network, our proposed Da-TRASH model is able to operate in environments and on robotic platforms where depth sensors are inadequite or unavailable. Thus, this project enables unseen object instance segmentation to be applicable in a broader range of robotic use cases. The proposed Da-TRASH model is validated on real-world trash segmentation datasets and results demonstrate the model achieves improved segmentation accuracy over existing models when depth data is unavailable.
Experiments
The proposed Da-TRASH pipeline is validated on multiple real-world datasets for both its qualitative and quantitative UOIS accuracy. First, the segmentation accuracy of Da-TRASH is qualitatively evaluated on examples from the ZeroWaste dataset (Bashkirova et al., 2021) as shown in the following figure:

This result demonstrates promising performance by Da-TRASH for segmenting previously unseen objects from an extremely cluttered scene representative of recycling facilities. More details and examples are included in the full text.
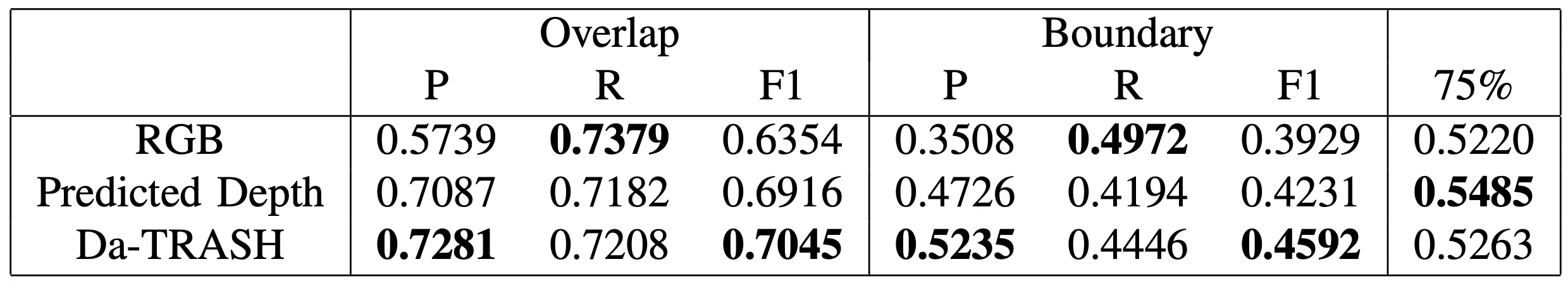
Based on the observed qualitative segmentation results, we next set out to establish how the accuracy of Da-TRASH compares to an RGB-only baseline, which does not use estimated depth for producing segmentation output. To perform this comparison, the Object Segmentation Database (Richtsfeld et al., 2012) was chosen as it includes segmentation labels that can be used for quantitative evaluation. Results from this comparison are included in the following table, showing Da-TRASH has improved accuracy according to the F1-score, over an RGB-only baseline and a depth-only baseline:
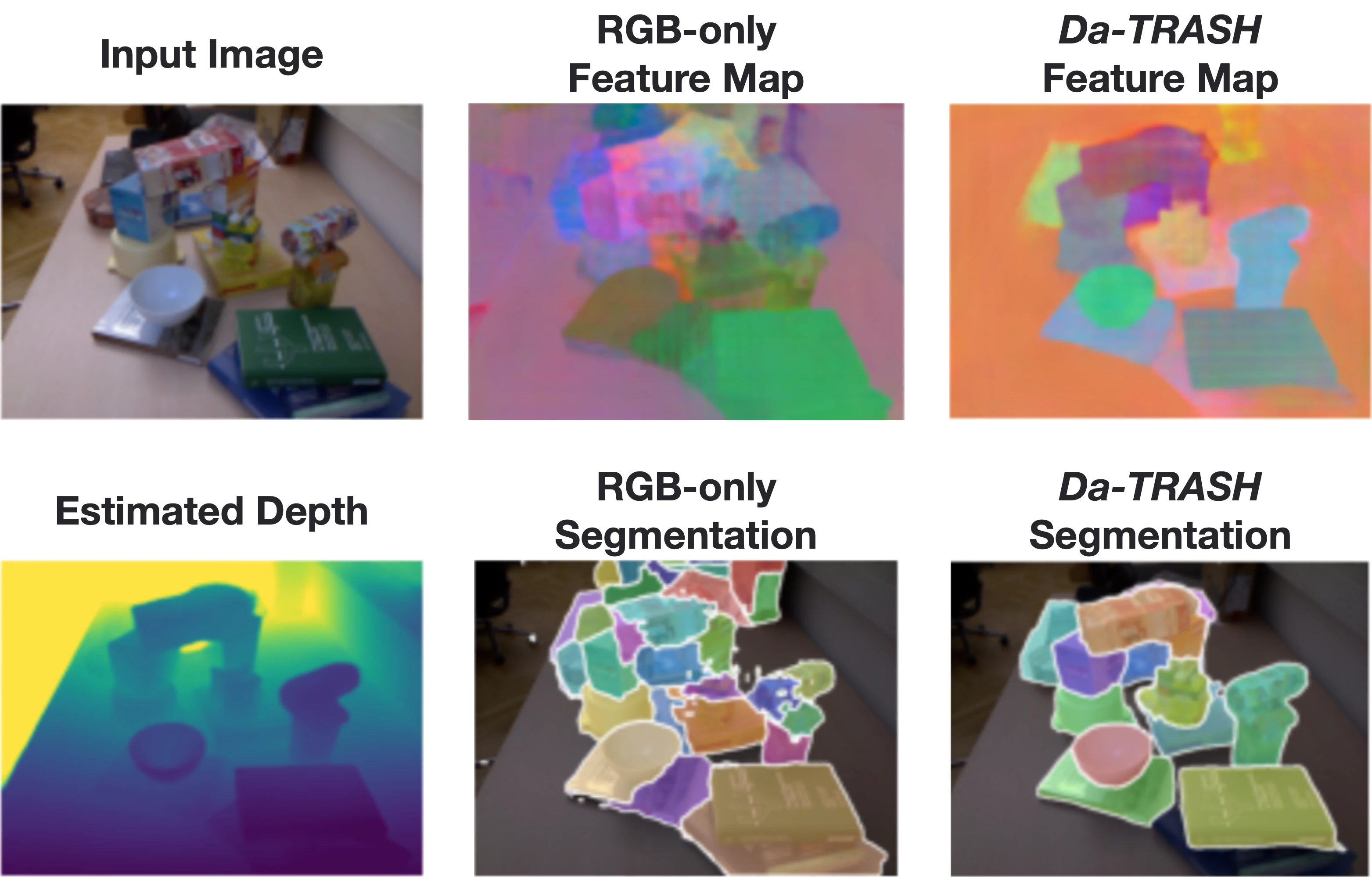
Moreover, qualitative results from this Object Segmentation Dataset are included below:
For additional details and experimental results, the reader is referred to the full project report.
Citation
If you found our work helpful, consider citing it with the following BibTeX reference:
@article{saxena2023da-trash,
title = {Da-TRASH: Depth-appended Tabletop Recycling Algorithm for Segmenting Havoc},
author = {Saxena, Ashwin and Scheffer, Andrew},
year = {2023}
}
Contact
If you have any questions, feel free to contact us.